Re-Wind

- Title
-
Re-Wind : Reuse and Recycling of Decommissioned Composite Material Wind Turbine Blades
- Start Date
-
January, 2018
- End Date
-
December, 2021
- Funding Body
-
Science Foundation Ireland, Department for the Economy (Northern Ireland), National Science Foundation (USA)
- Coordinator
-
University College Cork, Queens University Belfast, Georgia Tech
- Research Partners
-
City University of New York, Munster Technological University
- Principal Investigators
-
Paul Leahy, Gerard Mullally, Niall Dunphy
- Research Area
-
Offshore Renewable Energy, Circular Economy
- Website
Introduction
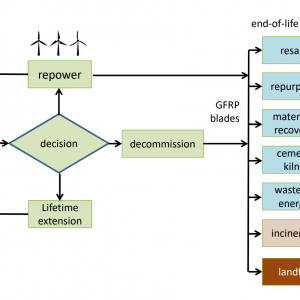
With the rapid development of wind energy technology in the past 15 years comes a new conundrum: how to dispose of the non-biodegradable blades in current wind turbines in a sustainable way. Annual Global Blade Waste Production is expected to reach 40 million tonnes by 2050. Conventional treatments for end-of-life wind turbine blades are not sustainable : these include landfill, incineration, waste-to-energy or co-processing in cement kilns. Repurposing blades to create new artefacts that are socially, environmentally and economically beneficial can avoid the negative impacts of these conventional disposal methods.
Aim
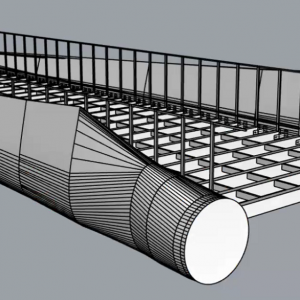
Our objective is to compare sustainable end–of–life reuse and repurposing strategies for composite material wind turbine blades using a Geographic Information Science (GIS) platform coupled with environmental, economic and social Life–Cycle Assessments (LCA). Our repurposing designs are designed and tested by experts in structural engineering and composites materials in the Re-Wind team.
Deliverables
- Viable repurposing options for end-of-life wind turbine blades
- Detailed environmental impacts analysis for blade repurposing compared to other end-of-life options
- Circular Economy Business Model analysis of wind turbine blade repurposing
- Community Engagement Methods to support sustainable local repurposing of wind turbine blades
Publications
-
Emma L. Delaney, Jennifer M. McKinley, William Megarry, Conor Graham, Paul G. Leahy, Lawrence C. Bank, Russell Gentry. An Integrated Geospatial Approach for Repurposing Wind Turbine Blades. In press at Resources, Conservation & Recycling March 2021
-
Deeney, P. and Nagle, A.J. and Gough, F. and Lemmertz, H. and Delaney E.L. and McKinley, J. and Graham, C. and Mullally, G. and Dunphy, N.P. and Leahy, P.G.
“Multi-criteria Decision Analysis using the Sustainable Development Goals for end-of life choices for wind turbine blades” In revision for Resources, Conservation & Recycling March 2021 - Gentry, T. R.; Al-Haddad, T.; Bank, L.C.; Arias, F.R.; Nagle, A.; Leahy, P.
‘Structural Analysis of a Roof Extracted from a Wind Turbine Blade’ ASCE Journal of Architectural Engineering 26(4). doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)AE.1943-5568.0000440
- Nagle, A. J. and Bank, L. and Leahy, P.G. (2020)
‘A Comparative Life Cycle Assessment Between Landfilling and Incineration of Waste from Decommissioned Irish Wind Turbine Blades’ Journal of Cleaner Production 277, 123321 doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123321
Engagement and Outreach
Re-Wind featured at New York City’s Town+Gown web event “New Frontier for Construction Materials—Decommissioned Wind Blades” in March 2021. This event, the 7th in the NYC Town+Gown Urban Resource Recovery (formerly Construction+Demolition Waste) series of events, introduced, to City and State agency members of the Town+Gown community, the topic of wind turbine blade second-life and sustainability of the wind industry, its challenges and its opportunities for both public agencies and private industry.
Re-Wind BladeBridge in Cork featured on EnergyLiveNews
Angela Nagle and Larry Bank quoted in recent Grist Article entitled “Today’s wind turbine blades could become tomorrow’s bridges.”
Contact
Email – ei.ccu@yhael.luaP
Photo Gallery